Describe Dominant and Recessive Alleles Providing Examples From Mendel's Work
If both alleles at a given locus are the same then from the standpoint of the particular gene this is termed a homozygote individual a homozygote. We often designate dominant alleles with a capital letter and the recessive allele with the corresponding small letter.
Introduction To Heredity Review Article Khan Academy
See also Gene interactions.

. He selected homozygous tall TT and dwarf tt pea plants. Blood type A and B are both dominant Mendel believed that you can not be both Pleiotropy. One gene has multiple effects on the physiology of an organism one gene multiple traits sickle-cell disease.
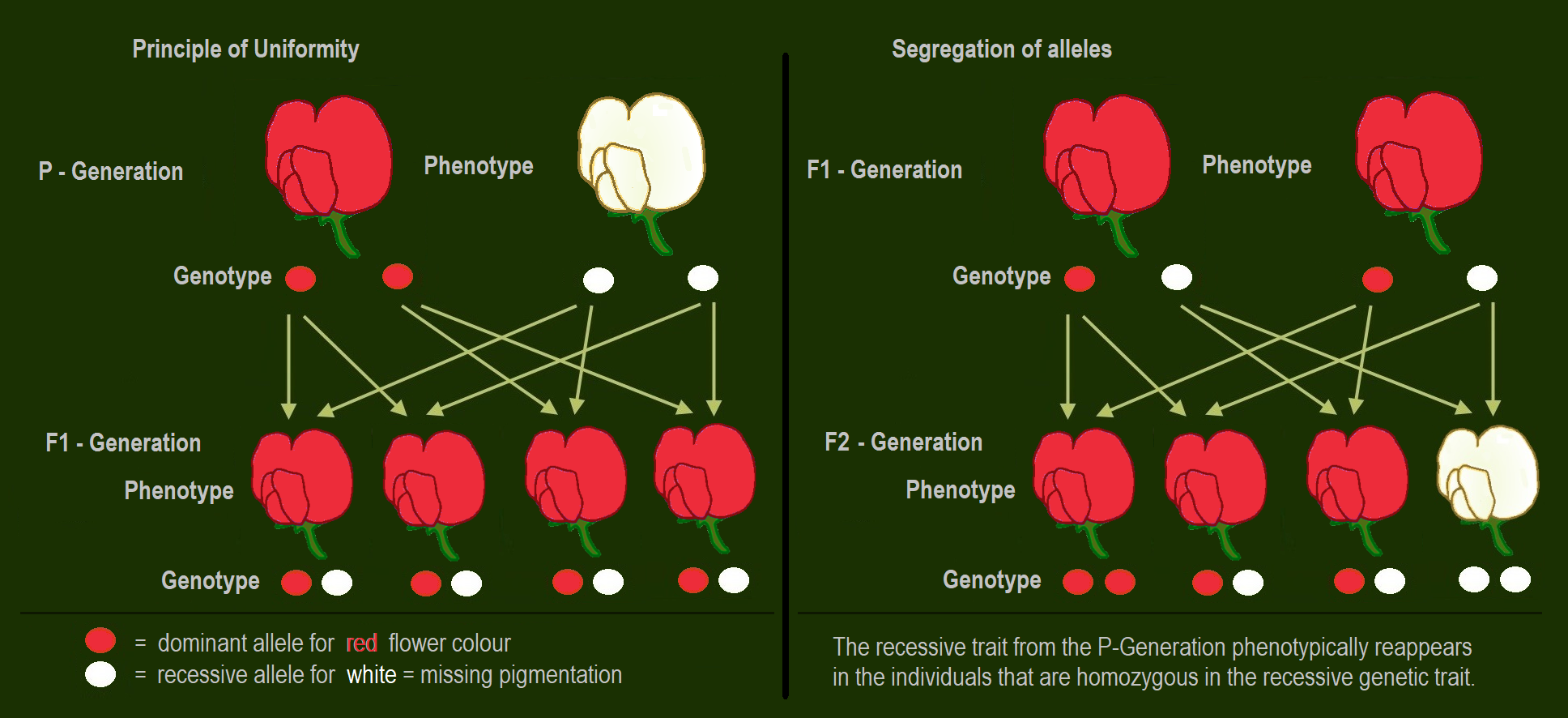
A parent cell makes gametes through the process of mitosis. Recessive allele recessive allele recessive phenotype. Mendel crossed two plants one having purple flowers and the other white flowers.
Dominant and Recessive Alleles. But you would probably be wrong. Describes Mendelian inheritance patterns and the relation between genotype and phenotypes.
Using a letter of the alphabet show how each allele would be represented. Describe dominant and recessive alleles providing examples from mendels work. Recessive alleles can be present in a population at very high frequency.
Describe the differences between Dominant and Recessive alleles. In case of plants there are many dominant alleles. Two forms of a gene - Dominant Recessive.
Patients with the 45X karyotype also written as 45 XO to denote. Describe dominant and recessive alleles providing examples from mendels work Well firstly alleles are different versions of genes. Mendels experiment itself has 7 characteristics which he worked on.
Albinism lack of pigment in the skin hair and eyes. Mendel conducted the experiments using Pisum sativum or pea plant. The Turner syndrome monosomy of the sex chromosome pair is a genetic disease caused by aneuploidy of the sex chromosome in humans.
Mendel counted the number of second-generation F2 progeny with dominant or recessive traits and found a 31 ratio of dominant to recessive traits. He crossed the tall pea plant with the dwarf pea plant. Explain the difference between dominant recessive alleles.
Not going to show the full dominant trait A red and white flower reproduce create a pink flower Co-Dominance. Dominant phenotypes will manifest when either or both chromosomes have the same dominant alleles whereas recessive phenotypes will only manifest when both chromosomes have the same recessive alleles. When allele pairs are the same they are homozygousWhen the alleles of a pair are heterozygous the phenotype of one trait may be dominant and the other recessive.
Dominant allele recessive allele dominant phenotype. A dominant allele will show its trait regardless of if the organism only has one copy of the allele heterozygous. An allele is said to be dominant when it overpowers other alleles.
Incomplete dominance occurs when the recessive allele is not completely dominant. In a cross between two homozyg ous dominant individuals 25 of the offspring may have the recessive phenotype. For example if we consider the dominant allele as A and recessive allele as a then in the case of homozygous we can write the two alleles as AA.
It is entirely likely for a gene to have more than two alleles. Recessive Inheritance - Two recessive alleles are needed to show disease heterozygous parents are carries of the disease-causing allele and the probability of inheritance increases with inbreeding mating between close relativesExample. Diploid organisms have two alleles from each gene.
When pure-bred parent plants were cross-bred dominant traits were always seen in the progeny whereas recessive traits were hidden until the first-generation F1 hybrid plants were left to self-pollinate. A dominant allele might be recessive in the presence of another dominant allele. It was observed that the F 1.
Dominant and recessive relationships are the best known forms of gene interaction between alleles within a single locus. Also discus Genotypes vs Phenotypes and Heterozygous vs Homozygous. Looking at this you might conclude that the dominant phenotype is twice as common as the recessive one.
Dominance is a relative trait for alleles. Diploid organisms typically have two alleles for a trait. In the case of heterozygous we can write it as Aa.
We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. Two heterozygous purple flowers have 75 chance of producing purple flowers and a 25 chance of producing a white flower. Provide examples of each.
Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. In both situations the dominant allele can express its phenotype over recessive allele. A dominant allele can hence express itself in both heterozygous and homozygous situations.
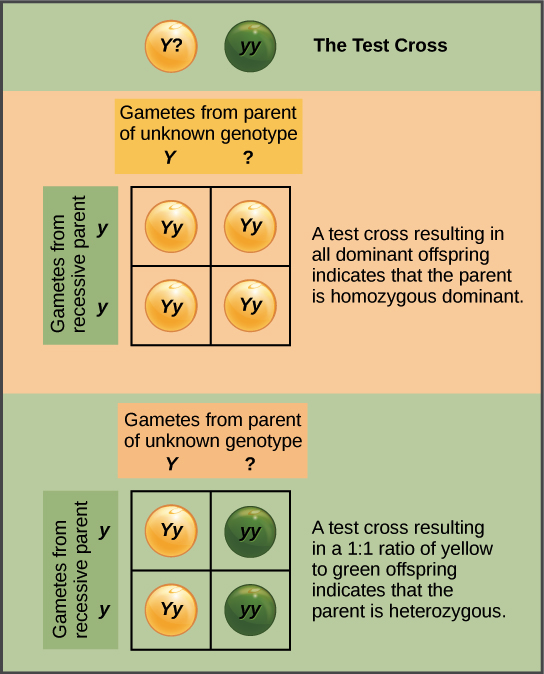
Use appropriate academic vocabulary and clear and complete sentences to predict the possible off springs and describe dominant and recessive alleles providing examples from Mendels work and from the diagram above. Dominance can be of three types. Generation are all tall plants.
Complete Dominance-When a dominant allele completely hides the effect of a recessive allele. Describe dominant and recessive alleles providing examples from mendels work Asked by wiki 26112021 in Biology viewed by 123 persons What are. For example the allele for brown eyes is dominant because if you have this allele then you will have brown eyes.
Alternative versions of a gene are called as alleles and they account for the variation in traits. Examples of dominant alleles in pea plant Pisum sativum are Red flower over White Round seed over wrinkled Axial. A recessive allele will show the effect only if two copies of.
The dominant allele is expressed and the recessive allele is masked. Dominant is stronger and will show up with a better chance than recessive.

Recessive Genetics Alleles Genes Traits Expii

What Are Dominant And Recessive Alleles Facts Yourgenome Org

Comments
Post a Comment